Dacha Vitamin C
Everything You Need to Know About Vitamin C
Medically Reviewed by Madeline Hubbard, RN, BSN.

Photo Courtesy: Flashpop/DigitalVision//Getty Images
Whether in the form of a fizzy drink or flavored lozenges, cold and flu preventative supplements almost always highlight vitamin C as one of their key ingredients. So, what's so magical about vitamin C? Also known as ascorbic acid, vitamin C is critical to living healthily. Since the human body cannot spontaneously generate this nutrient, vitamin C must instead be absorbed from outside sources, such as vitamin supplements or foods that are naturally rich in it.
What Does Vitamin C Do?
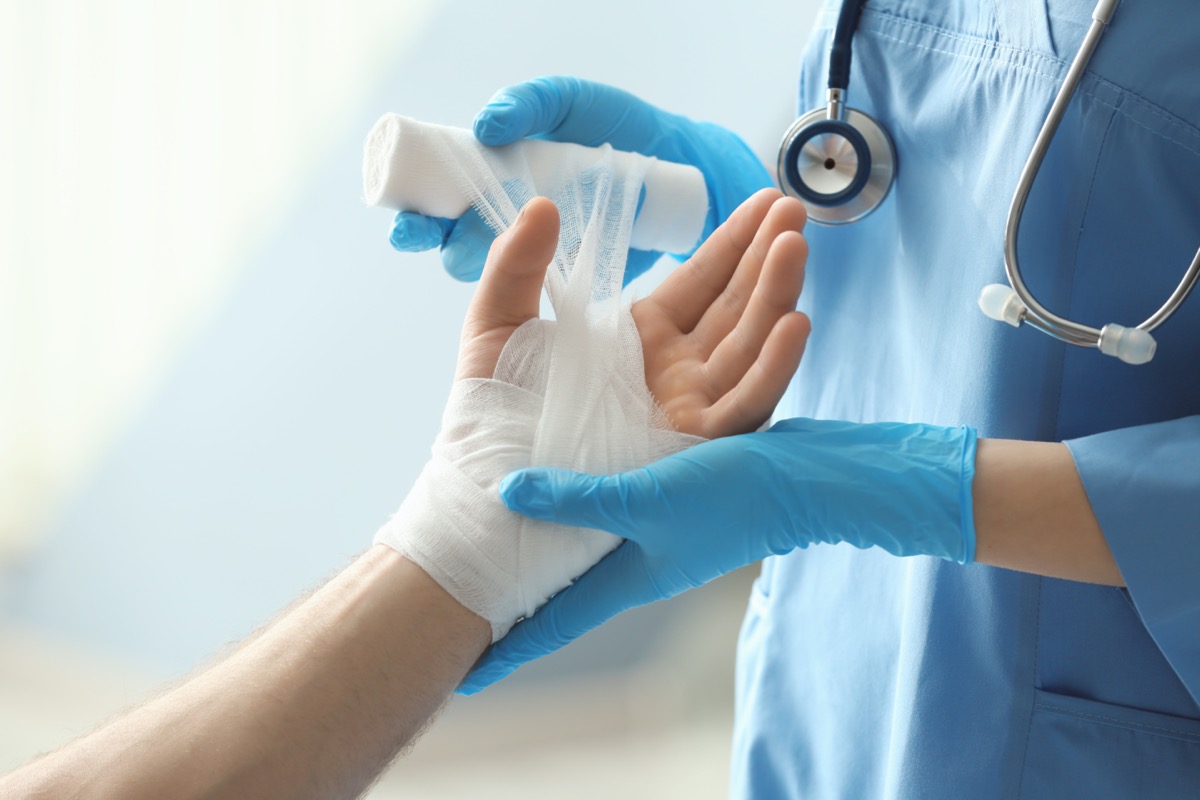
Commonly found in cold and flu preventative supplements, vitamin C strengthens and speeds up immune system functionality. Though research does not indicate that vitamin C intake alone can prevent the onset of cold or flu, adequate daily intake may shorten the duration of an infection or lessen the severity of symptoms.

Photo Courtesy: Catherine Falls Commercial/Moment/Getty Images
Vitamin C is crucial for the maintenance of well being. For example, it plays a role in wound healing and helps maintain many essential body tissues. It also acts as a potent antioxidant and can repair damage from free radicals, which are linked to aging effects, and disease vulnerability. Additionally, vitamin C can also prevent anemia, since it helps the body increase absorption of dietary iron, another vital mineral that the body cannot spontaneously create.
Foods that contain high concentrations of vitamin C have been linked with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, like heart attack and stroke. Vitamin C can also increase levels of nitric oxide, a compound that widens blood vessels and, in turn, lowers blood pressure. In addition, regular intake of vitamin C, along with other vitamins, has been linked to a decreased risk for developing age-related cataracts, a leading cause of visual impairment in the United States.
Common Sources of Vitamin C
Vitamin C can be easily obtained through the many different foods, including:

Photo Courtesy: Akaradech Pramoonsin/Moment/Getty Images
- Citrus fruits and juices (orange, grapefruit, lemon, lime and tangerine)
- Berries
- Melons
- Mangoes
- Kiwi
- Tomato
- Broccoli
- Red peppers
- Spinach
- Squash
- Potatoes
Cooking these foods may result in the loss of some of the vitamin content, so it is ideal to ingest them raw, either whole or juiced. Nowadays, there are also numerous packaged food products, like cereals, that have been enriched and fortified with vitamin C, so that the nutrient can be easily obtained.
Vitamin C may also be labeled as "L-ascorbic acid" in supplement form, and most over-the-counter multivitamins contain the recommended daily amount of the vitamin. While it is a good source when an individual is in need of a vitamin C boost, supplements are not meant to replace a diet rich in naturally derived vitamin C.
What Happens When You Have Too Much — or Too Little — Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that can be easily flushed out of the body via urination when it is not needed. Therefore, if the main source of vitamin C is from naturally occurring foods, it is near-impossible for excess vitamin C to produce side effects. However, taking excessive concentrated vitamin C supplements may lead to diarrhea or stomach upset.

Photo Courtesy: Violeta Stoimenova/E+/Getty Images
Since vitamin C-rich foods are so readily available nowadays, symptoms of inadequate vitamin C intake are also rare in the United States. However, malnourished individuals can experience symptoms of vitamin C deficiency over time, including:
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Anemia
- Easy bruising
- Joint pain
- Skin breakdown
- Weakened tooth enamel
- Gum inflammation
Severe vitamin C deficiency is referred to as scurvy. Scurvy can be easily treated with increased dietary or supplemental vitamin C. Since vitamin C is crucial in the detoxification of the body, a lack of vitamin C can compromise the immune system and make an individual more susceptible to diseases and infections. Individuals with insufficient vitamin C may find that it takes longer than usual to recover from a cold or a physical wound.
Daily Dosage Recommendations:
The daily dosage recommendation for vitamin C is different for everyone, depending on factors such as gender, age, lifestyle and current health condition. The recommended daily dosage for vitamin C is at least 75 mg daily for women and 90 mg for men. Since people who are pregnant, breast feeding, smoking or using oral contraceptives have a lower blood level of vitamin C than others, larger doses of vitamin C may be needed to achieve optimal results in these individuals. Those who have prior or current medical conditions may also require bigger or smaller dosage levels, as recommended by their healthcare providers.
Resource Links:
- "Vitamin C" via MedlinePlus
- "Vitamin C and Infections" via MDPI
- "Extra Dose of Vitamin C Based on a Daily Supplementation Shortens the Common Cold: A Meta-Analysis of 9 Randomized Controlled Trials" via Hindawi, BioMed Research International
- "Vitamin C" via National Institutes of Health
- "Scurvy" via U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, National Institutes of Health
- "Dietary intake and blood concentrations of antioxidants and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies" via The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- "Dietary vitamin and carotenoid intake and risk of age-related cataract" via The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- "Cardiovascular System" via Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine (via Springer)
More From SymptomFind.com
Source: https://www.symptomfind.com/health/vitamin-c-everything-you-need-to-know?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740013%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex