Taking Vitamin C
Vitamin C, aka L-ascorbic acid, is naturally present in some foods, added to others, and also available as a dietary supplement, explains the National Institutes of Health—but do you know what taking vitamin C every day does to your body? According to Darren Mareiniss, MD, FACEP , Emergency Medicine Physician at Einstein Medical Center in Philadelphia, the vitamin is essential to every diet—and knowing what taking vitamin C every day does to your body is important. "Vitamin C is naturally present in many foods and is not synthesized by the body," he explains to Eat This, Not That! Health. "It must be ingested." Food sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, peppers, Brussels sprouts, tomatoes, cantaloupe, potatoes, strawberries, and spinach. However, some people prefer taking it in supplement form. Read on to find out more—and to ensure your health and the health of others, don't miss these Sure Signs You May Have Already Had COVID.
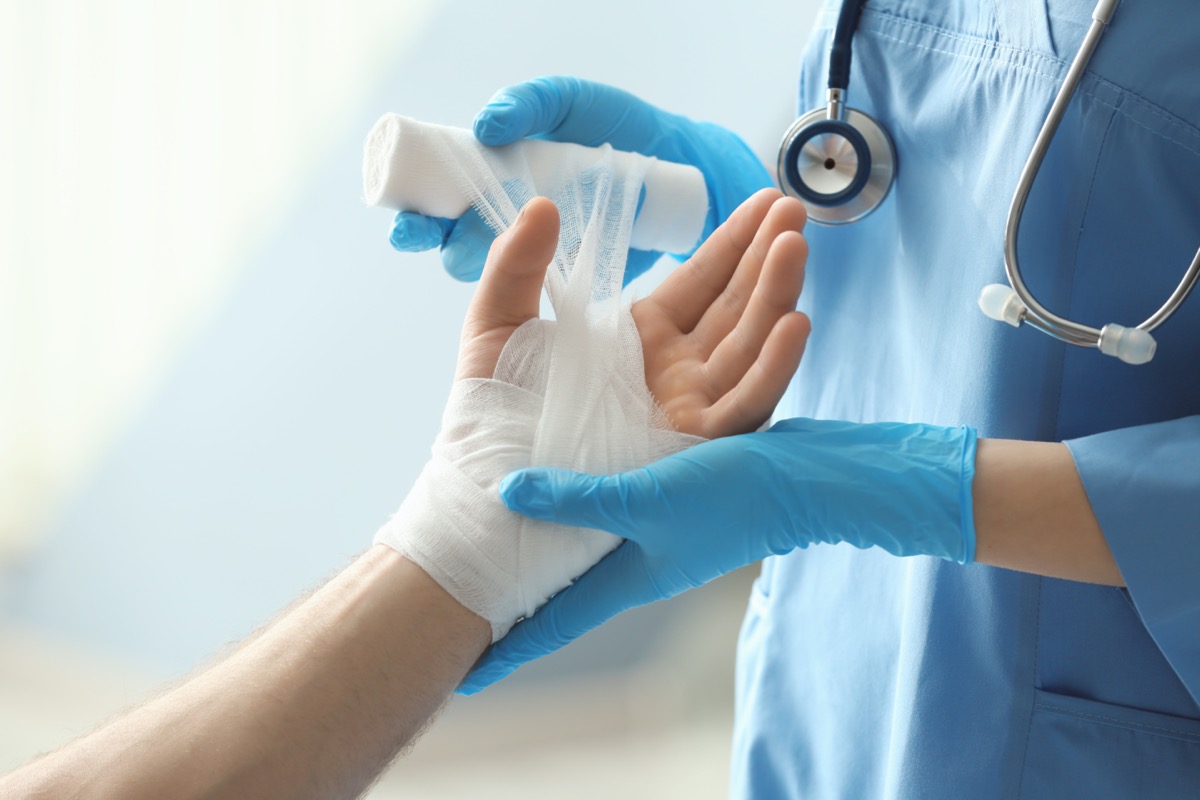

"Vitamin C is an essential component of connective tissue and plays a role in wound healing," says Dr. Mareiniss.
RELATED: Signs You're Developing Dementia, According to a Doctor

Dr. Mareiniss explains that Vitamin C is an antioxidant, meaning they can help prevent cell damage. Therefore, it can help prevent health issues where oxidative stress plays a role.
RELATED: Simple Ways to Never Get Sick, According to Doctors

Dr. Mareiniss explains that Vitamin C "is required for the biosynthesis of collagen." This is why it is a key ingredient in many skincare products.
RELATED: Sure Signs You're Becoming Obese, According to Science
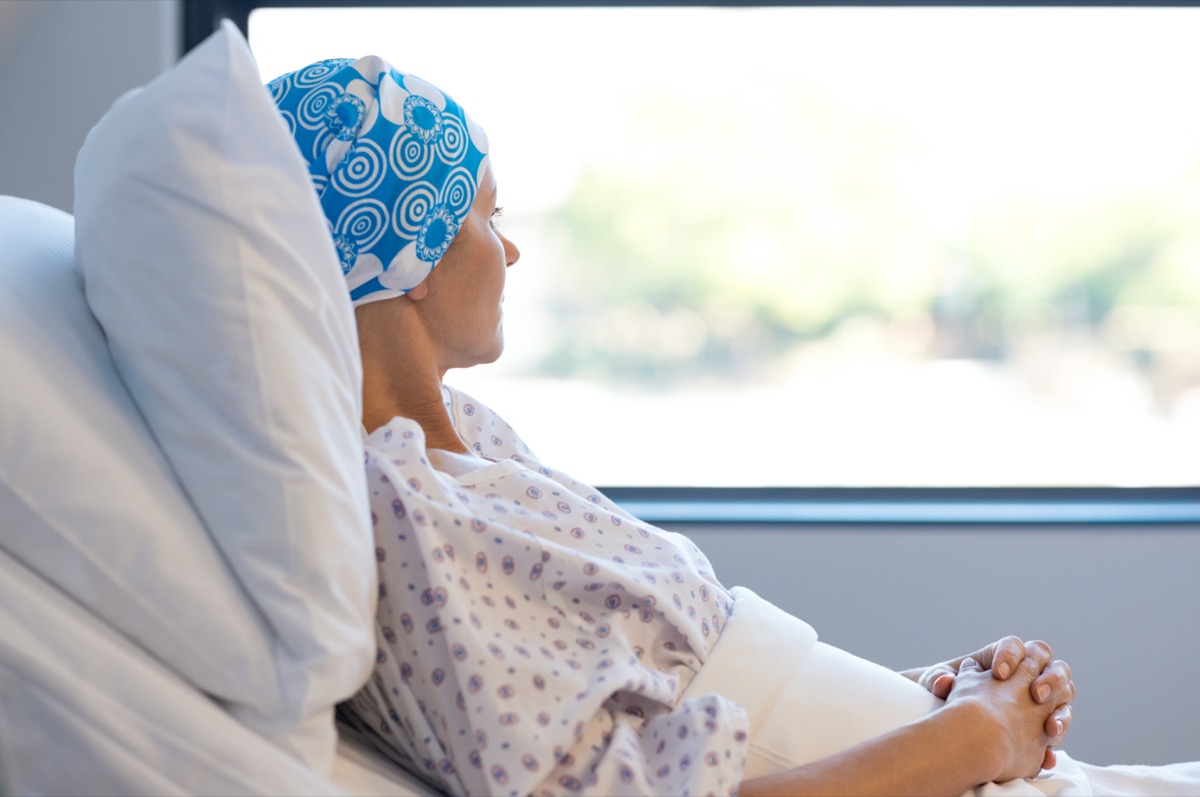

Per the NIH, there is an abundance of research supporting that vitamin C can help keep cancer at bay. "Most case-control studies have found an inverse association between dietary vitamin C intake and cancers of the lung, breast, colon or rectum, stomach, oral cavity, larynx or pharynx, and esophagus," they reveal.
RELATED: The Easiest Way to Live Longer, Says Science

According to the NIH, there is some evidence that vitamin C can help keep cardiovascular disease at bay. One of the largest studies , involving over 85,000 women, found that intake of vitamin c in both dietary and supplemental form reduced the risk of coronary heart disease. Others have found it can reduce the risk of stroke.
RELATED: Best Way to Boost Your Immunity Now, Says Science

The NIH also offers compelling evidence that vitamin c may help prevent and even treat age-related macular degeneration and cataracts, the two leading causes of vision loss in older people.
RELATED: The #1 Reason People Get Obese, According to Science
According to the NIH and Dr. Mareiniss, acute vitamin C deficiency can lead to scurvy. "This is very rare in developed countries," he explains. Signs of scurvy can appear within a month of vitamin c deficiency. Initial symptoms include fatigue, Malaise, and inflammation of the gyms. However, the condition can worsen to include depression, swollen bleeding gums, and the loosening and loss of teeth. If left untreated it can be fatal.
RELATED: The Unhealthiest Supplements You Should Not Take

Vitamin C is commonly thought of as an immune booster. However, the NIH points out that it might not be as effective in preventing a cold as you would think. Vitamin C can help shorten the duration of the common cold, says Dr. Mareiniss. "Vitamin C supplements might shorten the duration of the common cold and ameliorate symptom severity in the general population" possibly due to the anti-histamine effect of high-dose vitamin C," explains the NIH.
RELATED: Simple Ways to Live to 100, Say Experts

While vitamin C has low toxicity and therefore, doesn't cause serious adverse effects at high intakes However, it can cause gastrointestinal disturbances — including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps.
RELATED: New Danger Sign You'll Get Alzheimer's Early, Says Study

There is some conflicting evidence that high amounts of vitamin C could "increase urinary oxalate and uric acid excretion" which could contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
RELATED: Major Health Secrets After 60, Say Experts

Vitamin C aids your body in iron absorption. One study found that just 100mg of vitamin C can improve the absorption of the blood building mineral by 67%. As for yourself, consider whether you're getting enough vitamin C, and to get through this pandemic at your healthiest, don't miss these 35 Places You're Most Likely to Catch COVID .
Source: https://www.eatthis.com/news-vitamin-c-every-day-body/








Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar